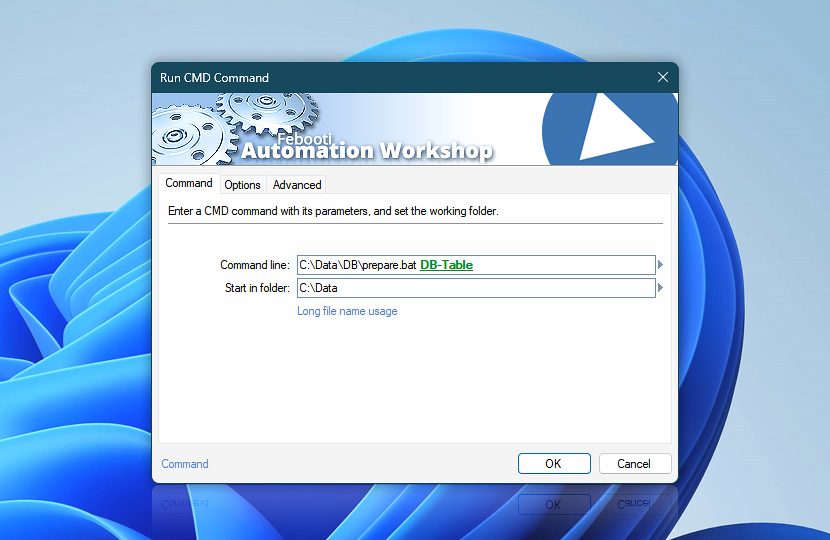
Enter a CMD command with the necessary parameters and the folder in which it will be executed. Running a CMD command works the same way as if the Windows command line interpreter cmd.exe were opened and the command were subsequently typed in.
| Command | Details |
|---|---|
| Command line | Specify a CMD command followed by necessary parameters and switches. Specifying batch files or Windows executables is also allowed. |
| Start in folder | Provide a disk location / path in which the specified CMD command, batch file or Windows executable will be executed. |
| Browse | |
| Variable Wizard |
Interconnect
- Run CMD Command integration and auditing—Variables (dynamic data) and Events (recorded activity). Retrieve the error level and PID of the recently completed CMD command, including the entire command line and the startup folder used.
Additionally, logs contain detailed information, warnings, and error events, highlighting the CMD command initiation and termination, as well as custom-defined success or failure levels.
Notes
- If a long filename is used to specify a command line parameter, put it into double quotes, e.g.,
"my file.txt". - Long filename usage · explains the necessity of delimiting long filenames using double quote characters.
- Always force placing new windows in the foreground (above all other windows). See simple instructions for a fix—New program window appears behind all other open windows.
Just ask…
If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact our support team.